What Marketers Must Know About URLs

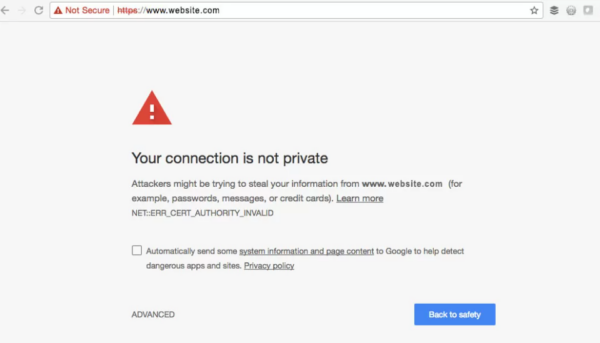
We have discussed Vanity URLs and their role in marketing, and one point that was missing from that post was the importance of URL security. Marketers should understand the differences between HTTP (non-secure) and HTTPS (secure) URLs, as these distinctions can impact website performance, security and user trust. It especially impacts security and user trust wherever non-secure links are used in digital marketing, such as email marketing where email server spam filters look for insecure links before bouncing, quarantining or routing the email to a user’s inbox.

Here are the most important things for marketers to know:
- Security: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a secure version of HTTP. It encrypts the data transmitted between a user’s browser and the website server, making it much more difficult for malicious actors to intercept or tamper with the information. Marketers should emphasize that HTTPS helps protect user data, such as login credentials and payment information, which can build trust with website visitors.
- Trust and Credibility: Websites with HTTPS URLs are often considered more trustworthy and credible by users. Browsers display a padlock icon in the address bar when a site uses HTTPS, indicating a secure connection. Marketers can leverage this trust factor in their messaging and promote the site’s commitment to security.
- SEO Impact: Google has been giving preference to HTTPS websites in its search rankings since 2014. Marketers should be aware that having an HTTPS URL can positively influence a site’s search engine visibility, potentially leading to higher organic traffic.
- User Experience: HTTPS can improve the overall user experience. Secure websites tend to load faster and are less prone to security-related issues. Marketers can emphasize the importance of a smooth and secure browsing experience to retain and engage users.
- Data Privacy: HTTPS is crucial for protecting user data privacy. Non-secure HTTP connections can expose user data to eavesdropping, which can lead to data breaches. Marketers should highlight the commitment to user privacy and data protection through HTTPS.
- Mixed Content Warnings: Non-secure HTTP elements (e.g., images, scripts) on a secure HTTPS page can trigger browser warnings. These warnings can scare off users, so marketers should work with developers to ensure all content is loaded securely.
- Migration Challenges: If a website is transitioning from HTTP to HTTPS, there can be temporary SEO and usability challenges. Marketers should plan and communicate these changes with users to minimize any potential disruptions.
- Cost and Certificate Renewal: HTTPS requires obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate, which may incur costs. Additionally, these certificates need periodic renewal. Marketers should be aware of these costs and ensure proper management to prevent disruptions in the website’s security.
- Performance Impact: While HTTPS is generally faster and more secure, it can slightly increase server load due to the encryption and decryption process. Marketers should work with their technical teams to optimize website performance while maintaining security.
- Legal and Compliance Considerations: Depending on the industry and location, there may be legal and compliance requirements regarding data security and encryption. Marketers should collaborate with their legal and compliance teams to ensure the website meets these standards.
HTTPS is not just a technical concern; it has a direct impact on user trust, website performance and SEO, even if the non-secure HTTP URL is only used as a redirect for attribution/analytics reasons in your digital marketing. Marketers should understand these implications and how their marketing campaigns might be impacted if driving traffic to a non-secure URL. An easy solution would be to register a domain of your choosing and have your team install an SSL certificate on the domain to make it secure, which will give you the best chances of a positive user experience (aka no browser security warnings!).
