Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Basics for Marketers

Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of improving a website to increase its search ranking. Search engines visit websites and follow links to build an index of all websites they encounter and use proprietary rules to calculate search ranking of a site for a specific search phrase. To increase the usefulness of search results and to discourage people from trying to game the system to improve their search ranking, search engines frequently change the rules that determine search ranking.
Search ranking is important because it is used when determining if a web page should be included in a list of search results, and where in that list it should appear.
While it takes an expert to keep on top of the latest changes, a number of SEO best practices will help one’s search ranking.
Submit Your URL to Search Engines
While a search engine may encounter your site by following links from other sites, you can be sure that your site is added to these search engine’s index by submitting your site directly to that engine, like:
-
- Bing
- Yahoo
You’re not able to submit your site to some search engines like DuckDuckGo because of their dedication to security and privacy. To submit your site to the search engines in the list above, you must do so by authenticating in with your username and password. Search engines dedicated to privacy can’t require a username and password to keep your personally identifiable information secure. They also can’t leave an open door for any internet user to submit sites to prevent abuse so they simply don’t allow submissions.
Write Descriptive Page Titles and Descriptions
Don’t be tempted to load your “title” and “meta description” tags in your code with lists of search terms. These HTML tags are the parts of your web page code that most search engines display in their search results. However, because web authors used to flood these tags with search terms, most search engines no longer use these tags when determining search ranking.
The current best practice is to write unique page titles and engaging descriptions for real humans, not search engines, so that when your page is included in a list of search results, web visitors are encouraged to visit your site because the titles and descriptions make sense to them.
Page Titles
These are added to the code between the title tags, but where they appear to web visitors is in the browser tab and the blue link headline in the search results page.
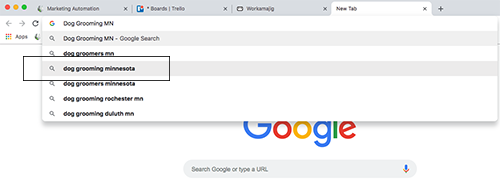
For example, let’s do a Google search for Dog Grooming Minnesota.
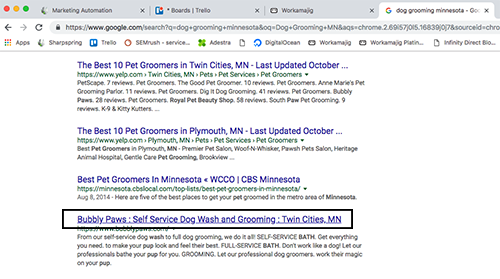
When I see the search results, as a web visitor, I’m looking for a result that makes sense to me. Bubbly Paws is a website found in the search results. What they have in their web page’s title in the code is what appears here in the hyperlinked blue headline.
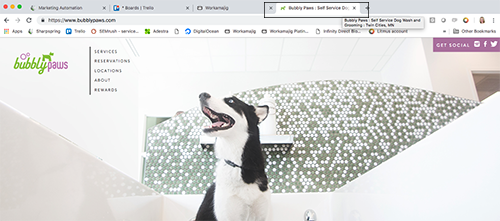
Once you click on the link and go to the website, the first thing you’ll notice is the text in the tab for that window in your browser. The same text that they have in their web page’s title in the code is what appears here in the tab at the top.
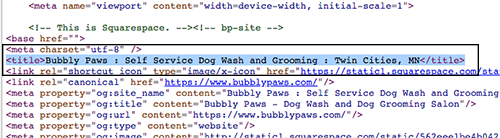
If you were curious where you would see this in the code, you can right click anywhere on the page and click “View Source” in the options. You would see the title tags toward the top and the text you saw in the search results and the text you saw in the browser tab will match the text inside the title tags.
Page Descriptions
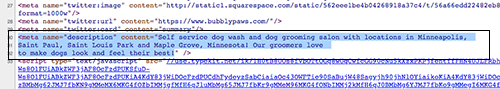 Just like title tags, there are also meta description tags in the code that tell search engines what to pull into the search results to describe the web page. In the absence of a meta description tag in the code or a website flooding the text inside the meta description with keywords that don’t match actual text on the site, most search engines will simply pull in the first paragraph of text it sees on the page like the following example where the meta description…
Just like title tags, there are also meta description tags in the code that tell search engines what to pull into the search results to describe the web page. In the absence of a meta description tag in the code or a website flooding the text inside the meta description with keywords that don’t match actual text on the site, most search engines will simply pull in the first paragraph of text it sees on the page like the following example where the meta description…
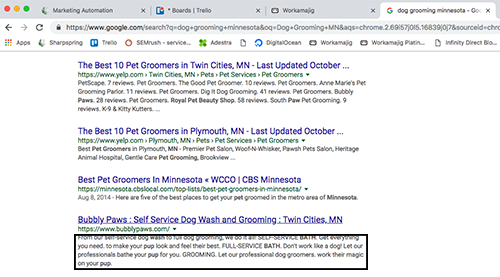 …is very different than what Google pulls in as the description. Google pulled in the first text it saw on the page instead.
…is very different than what Google pulls in as the description. Google pulled in the first text it saw on the page instead.
You can see that it is very important to Google that whatever text is in the meta description matches the text on the page or it will use text from the page and ignore your description.
Include Search Terms in your Text-Based Content
The way that search engines know whether to include your page in their list of search results is by finding the terms people use in their search engine in the text-based content of your website. Text-based content includes all the words on the page, the page title and the URL of the page. Keep the copy natural while including as many relevant search terms as possible.
If your web page has video or images, a web developer can help you include search terms with this content. Best practices for SEO of non-text elements like images and video are similar to those for web accessibility. Here’s a quick guide for some common content types.
Think about your links
Another SEO-boosting accessibility practice is to use descriptive labels for links. Since search engines create their indexes by following links between pages, it is important to include context in the visible text on your links. For example, if you have a contact page instead of using “To contact us, “click here” use “Contact us” or “Contact Infinity Direct.”
To increase the chances of search engine indexes including your pages, make sure your site’s pages link to each other using search terms where you can. If you maintain multiple sites, create links between them where appropriate. Encourage your partners to link to your content, too. But, wherever you can, avoid using the best search terms for your content when linking to content on external websites, because this adds to the search ranking of the external website instead of your own site.
